About Us
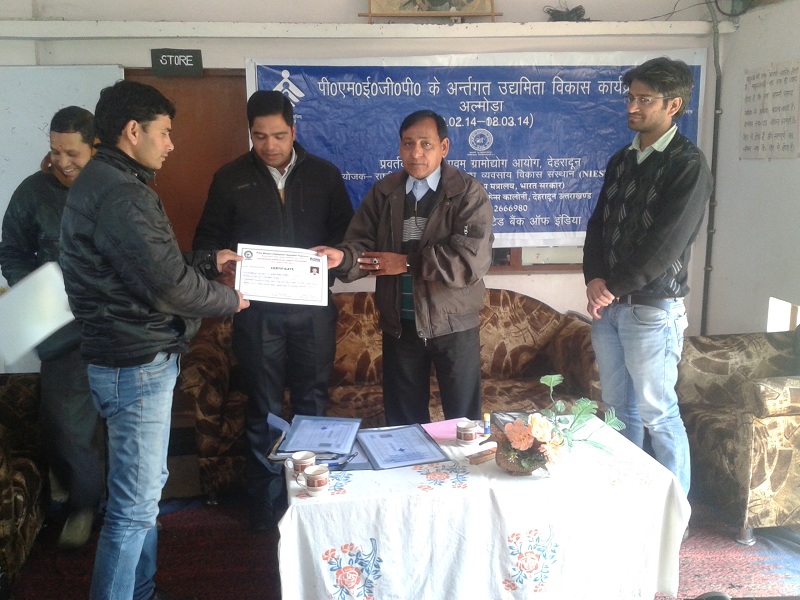
SPARDHA (Society for People’s Action and Rural Development in Himalayan Area) came into being in 1994 as a society under Society Act 1860, and since then it is engaged in the activities which enable rural people especially rural women folk to earn their livelihood. For this SPARDHA adopted promotion of bee keeping – Indica Cerena- in the region to bring extra income to the masses as well as to save the degrading environment which is an issue today. Society is committed to the socio-economic development of the region. Shri Deep Chandra Bisht, the secretary & Chief Functionary of the organization has taken up socio-economic development of the Himalayan region as a mission of his life to nurture it till it reaches its zenith. His zeal and enthusiasm was so intense that Mr. Bisht invested, Rs. 3,00,000/- , his own hard earned money, by serving the nation through Indian Navy, in 1994-1995 for procuring term loan and working capital to run the organization’s activities. At present the office of the organization is located at Ishwari Bhawan, Pokharkhali, Almora (Uttarakhand). The secretary of the organization in the building of his own house has spared this office. Since the honey procured from the members increased day by day, the organization felt it was necessary to install processing unit nearby the office of the organization. Hence, In 1997 the honey-processing unit was installed in the Industrial Estate, Patal Devi, Almora.
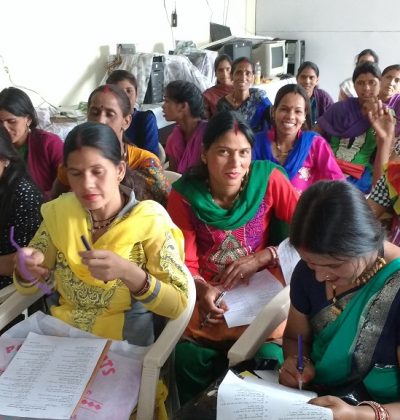
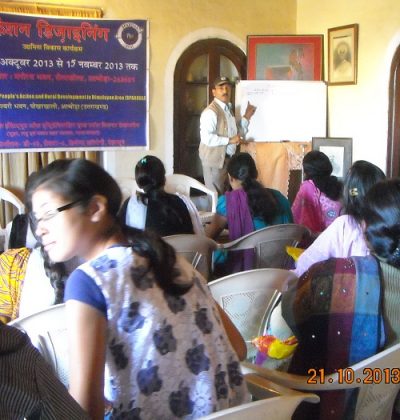
Women Empowerment
 Women empowerment, referring to the empowerment of women in our present society, has become a significant topic of discussion in regards to development and economics. It can also point to approaches regarding other marginald genders in a particular political or social context.
Women empowerment, referring to the empowerment of women in our present society, has become a significant topic of discussion in regards to development and economics. It can also point to approaches regarding other marginald genders in a particular political or social context.
While often interchangeably used, the more comprehensive concept of Gender empowerment refers to people of any gender, stressing the distinction between biological sex and gender as a role. It thereby also refers to other marginalized genders in a particular political or social context.
One way to deploy the empowerment of women is through land rights. Land rights offer a key way to economically empower women, giving them the confidence they need to tackle gender inequalities. Often, women in developing nations are legally restricted from their land on the sole basis of gender. Having a right to their land gives women a sort of bargaining power that they wouldn’t normally have, in turn; they gain the ability to assert themselves in various aspects of their life, both in and outside of the home.[1] Another way to provide women empowerment is to allocate responsibilities to them that normally belong to men. When women have economic empowerment, it is a way for others to see them as equal members of society. Through this, they achieve more self-respect and confidence by their contributions to their communities. Simply including women as a part of a community can have sweeping positive effects.
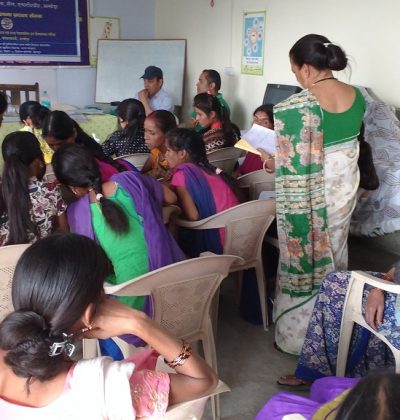
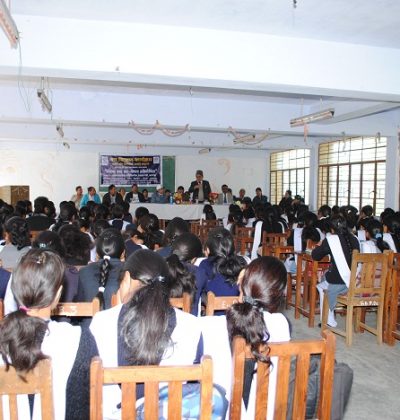
Education
 Education is the process of facilitating learning, or the acquisition of knowledge, skills, values, beliefs, and habits. Educational methods include storytelling, discussion, teaching, training, and directed research. Education frequently takes place under the guidance of educators, but learners may also educate themselves. Education can take place in formal or informal settings and any experience that has a formative effect on the way one thinks, feels, or acts may be considered educational. The methodology of teaching is called pedagogy.
Education is the process of facilitating learning, or the acquisition of knowledge, skills, values, beliefs, and habits. Educational methods include storytelling, discussion, teaching, training, and directed research. Education frequently takes place under the guidance of educators, but learners may also educate themselves. Education can take place in formal or informal settings and any experience that has a formative effect on the way one thinks, feels, or acts may be considered educational. The methodology of teaching is called pedagogy.
Education is commonly and formally divided into stages such as preschool or kindergarten, primary school, secondary school and then college, university or apprenticeship.
A right to education has been recognized by some governments, including at the global level: Article 13 of the United Nations’ 1966 International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights recognizes a universal right to education. In most regions education is compulsory up to a certain age.
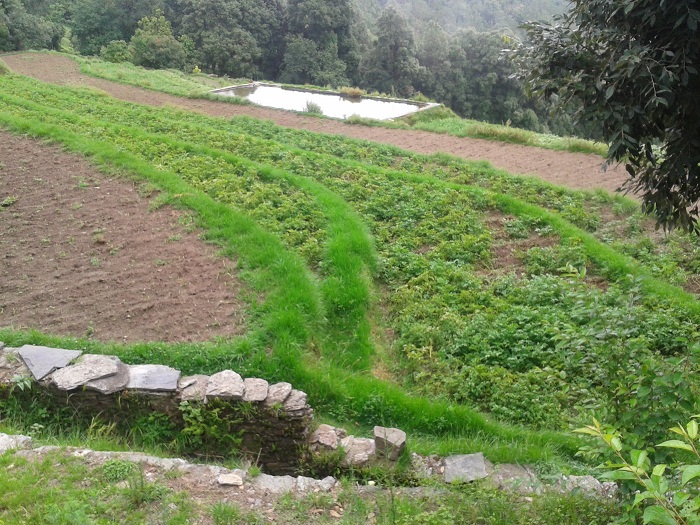
Rainwater harvesting
 Rainwater harvesting is the accumulation and deposition of rainwater for reuse on-site, rather than allowing it to run off. Rainwater can be collected from rivers or roofs, and in many places the water collected is redirected to a deep pit (well, shaft, or borehole), a reservoir with percolation, or collected from dew or fog with nets or other tools. Its uses include water for gardens, livestock, irrigation, domestic use with proper treatment, and indoor heating for houses etc. The harvested water can also be used as drinking water, longer-term storage and for other purposes such as groundwater recharge.
Rainwater harvesting is the accumulation and deposition of rainwater for reuse on-site, rather than allowing it to run off. Rainwater can be collected from rivers or roofs, and in many places the water collected is redirected to a deep pit (well, shaft, or borehole), a reservoir with percolation, or collected from dew or fog with nets or other tools. Its uses include water for gardens, livestock, irrigation, domestic use with proper treatment, and indoor heating for houses etc. The harvested water can also be used as drinking water, longer-term storage and for other purposes such as groundwater recharge.
Rainwater harvesting provides an independent water supply during regional water restrictions and in developed countries is often used to supplement the main supply. It provides water when there is a drought, can help mitigate flooding of low-lying areas, and reduces demand on wells which may enable groundwater levels to be sustained. It also helps in the availability of potable water as rainwater is substantially free of salinity and other salts. Application of rainwater harvesting in urban water system provides a substantial benefit for both water supply and wastewater subsystems by reducing the need for clean water in water distribution system, less generated stormwater in sewer system, as well as a reduction in stormwater runoff polluting freshwater bodies.
There has been a large body of work focused on the development of Life Cycle Assessment and Life Cycle Costing methodologies to assess the level of environmental impacts and money that can be saved by implementing rainwater harvesting systems.
Environment
 All life that has survived must have adapted to conditions of its environment. Temperature, light, humidity, soil nutrients, etc., all influence any species, within any environment. However life in turn modifies, in various forms, its conditions. Some long term modifications along the history of our planet have been significant, such as the incorporation of oxygen to the atmosphere. This process consisted in the breakdown of carbon dioxide by anaerobic microorganisms that used the carbon in their metabolism and released the oxygen to the atmosphere. This led to the existence of oxygen-based plant and animal life, the great oxygenation event. Other interactions are more immediate and simple, such as the smoothing effect that forests have on the temperature cycle, compared to neighboring unforested areas
All life that has survived must have adapted to conditions of its environment. Temperature, light, humidity, soil nutrients, etc., all influence any species, within any environment. However life in turn modifies, in various forms, its conditions. Some long term modifications along the history of our planet have been significant, such as the incorporation of oxygen to the atmosphere. This process consisted in the breakdown of carbon dioxide by anaerobic microorganisms that used the carbon in their metabolism and released the oxygen to the atmosphere. This led to the existence of oxygen-based plant and animal life, the great oxygenation event. Other interactions are more immediate and simple, such as the smoothing effect that forests have on the temperature cycle, compared to neighboring unforested areas
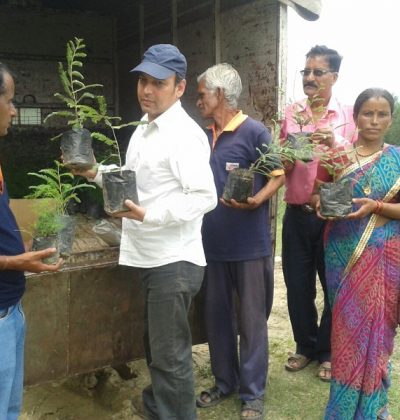
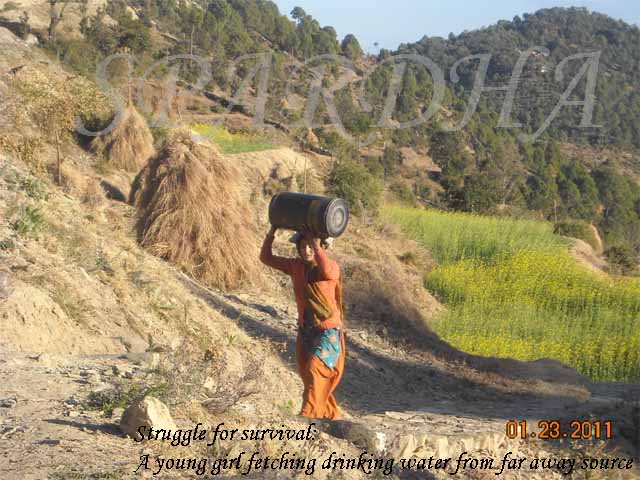
Natural Resources
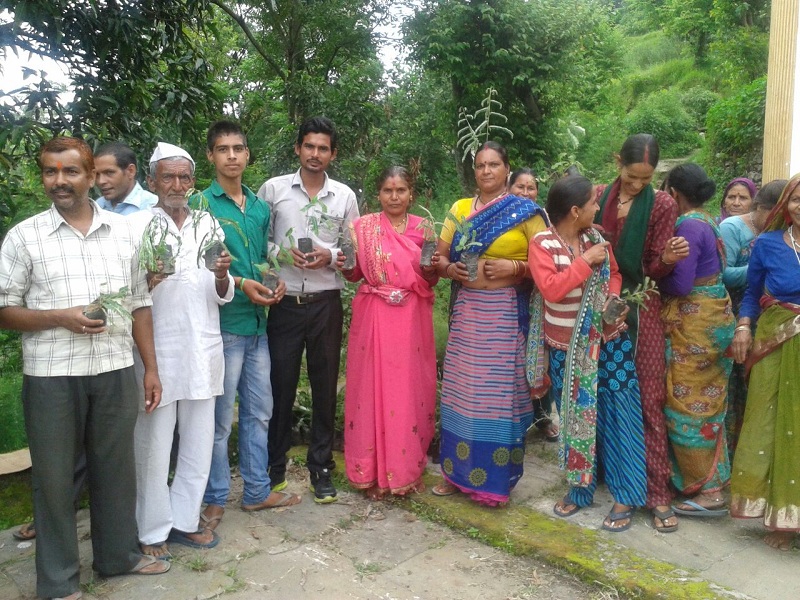
 Resources are features of environment that are important and value of to human in one form or the other. However, the advancement of modern civilization has had a great impact on our planet’s natural resources. So, conserving natural resources is very essential today. There are many ways that one can conserve natural resources. All you need to do is to look around and see what natural resources you are using and find out ways to limit your usage. Most of the people use natural gas to heat their water and their home. You can monitor how much you are using this resource to minimize its usage.
Resources are features of environment that are important and value of to human in one form or the other. However, the advancement of modern civilization has had a great impact on our planet’s natural resources. So, conserving natural resources is very essential today. There are many ways that one can conserve natural resources. All you need to do is to look around and see what natural resources you are using and find out ways to limit your usage. Most of the people use natural gas to heat their water and their home. You can monitor how much you are using this resource to minimize its usage.
For conservation of natural resources like natural gas, one can get tank less water heater as it reduces the usage of natural gas. The other way to save natural gas is the use of another energy source for instance hydro, solar or wind power are all healthy and great alternatives to conserving natural resources. In fact these energy sources are clean and healthy for environment. Moreover, these energy sources do not emit or produced harmful gases or toxin into our environment like that of the burning fossil fuels at the same time they are renewable as well as are not easy to deplete.